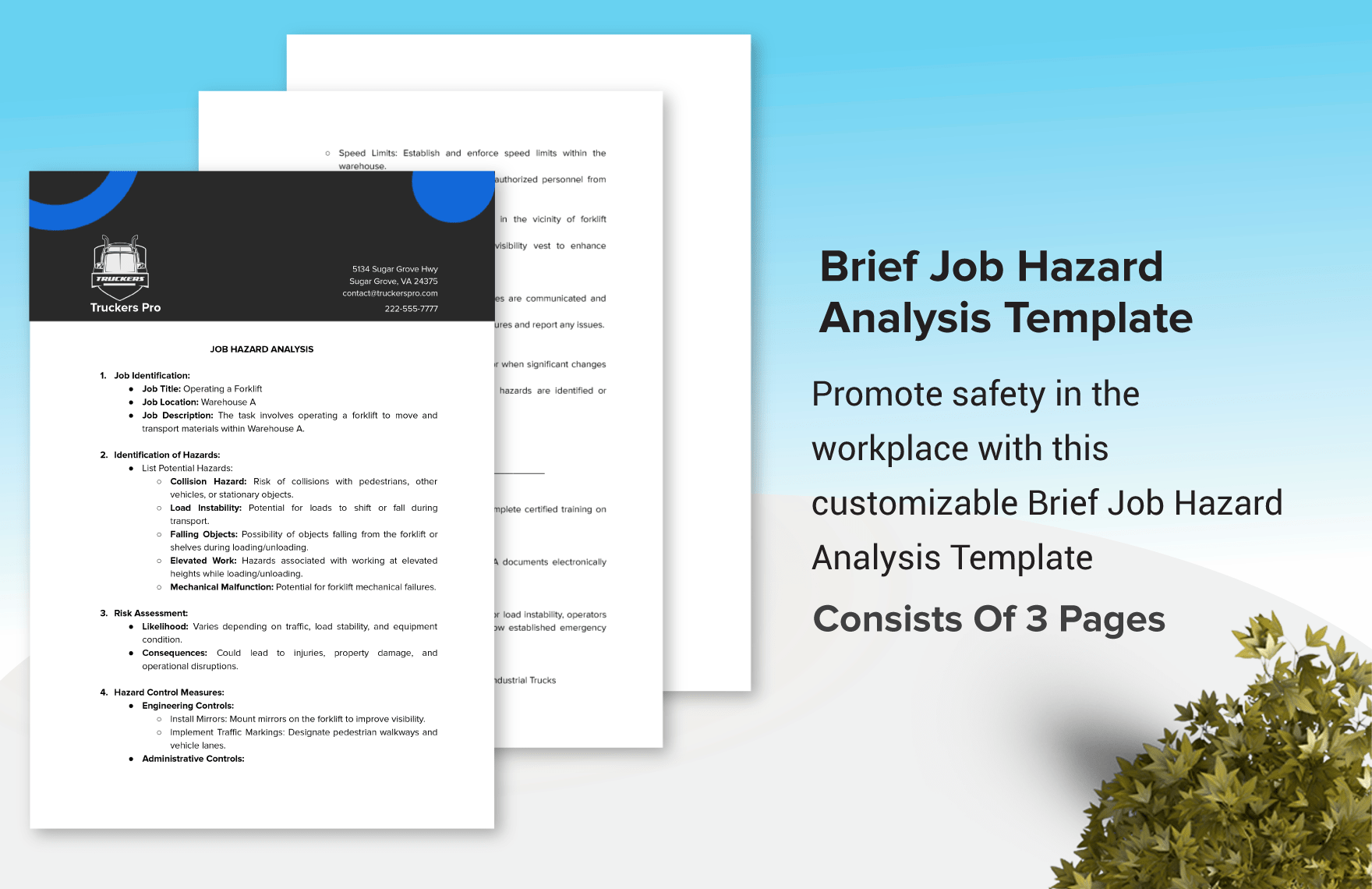
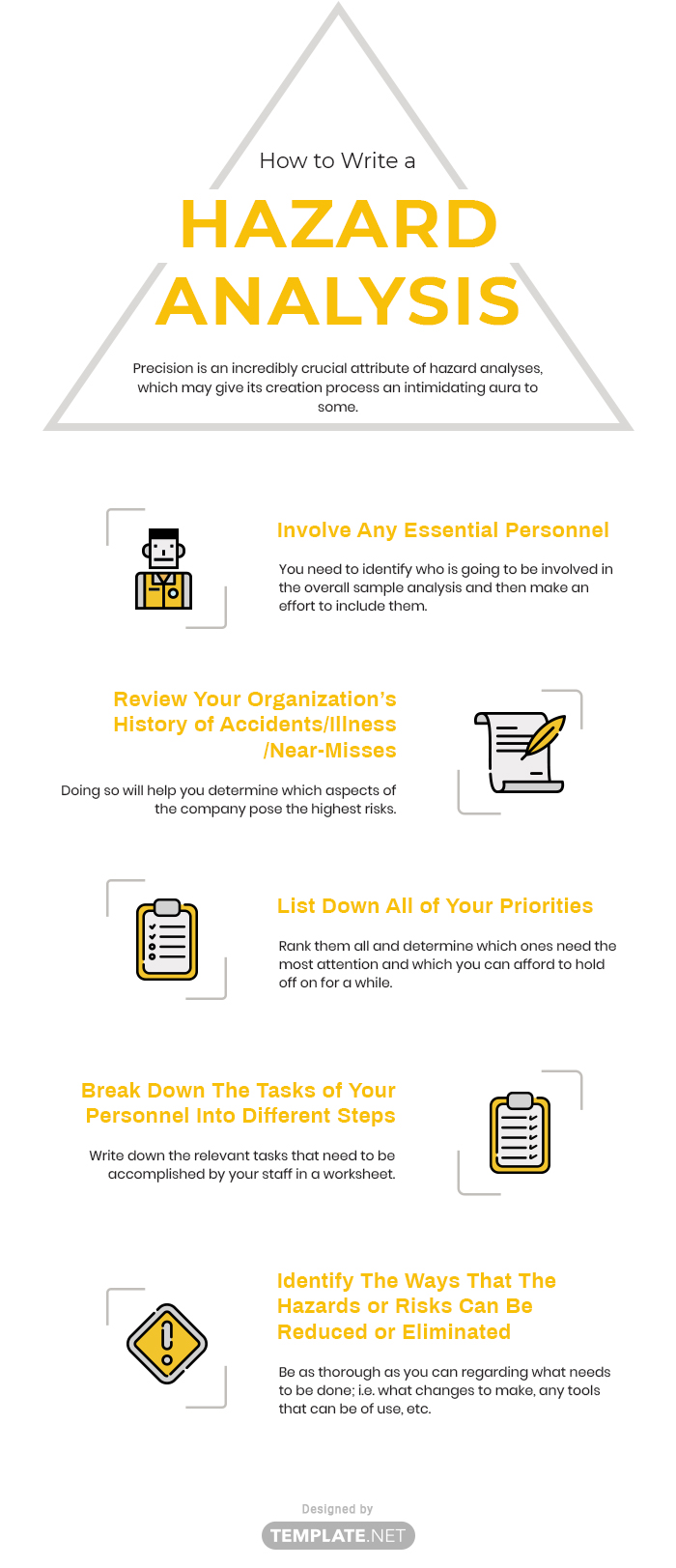
Precision is an incredibly crucial attribute of hazard analyses, which may give its creation process an intimidating aura to some. However, that does not exclude the possibility of a relatively easy and simple analysis experience on your part. Be assured that clear and concise instructions are perfectly within your reach, allowing for an easier time and a swifter creation process. With that said, take a close look at each of the following steps and see for yourself how well the overall results will be. After all, a worker is injured in the workplace every seven seconds; make sure this fate doesn't befall any of your workers.
1. Involve Any Essential Personnel
First of all, you need to identify who is going to be involved in the overall sample analysis and then make an effort to include them. A discussion regarding what it is that you are aiming to do and why it will prove necessary at a later date, but for now, this will do.
2. Review Your Organization’s History of Accidents/Illness/Near-Misses
Once you’ve identified and involved the essential personnel, the next step is to examine your organization’s history of accidents, illnesses, and near-misses. Doing so will help you determine which aspects of the company pose the highest risks.
3. List Down All of Your Priorities
Write down priorities that involve highest injury or illness rates, jobs, or positions with numerous ‘close calls’, positions where OSHA standard violations can be identified, and various others. Rank them all and determine which ones need the most attention and which you can afford to hold off on for a while.
4. Break Down The Tasks of Your Personnel Into Different Steps
Write down the relevant tasks that need to be accomplished by your staff in a worksheet. It can be listed down in a step-by-step manner to provide them with a more organized procedure. From there, you can discuss the findings of their tasks at a much later date.
5. Identify The Ways That The Hazards or Risks Can Be Reduced or Eliminated
The last step for you to undertake would be the identification of all the risks and hazards determined by the analysis sheet, as well as the means in which you can properly eliminate or reduce them. Be as thorough as you can regarding what needs to be done; i.e. what changes to make, any tools that can be of use, etc.